# 进程管理(重点)
# 基本介绍
1)在Linux中,每个执行的程序(代码)都称为一个进程。每一个进程都分配一个ID号。
2)在每一个进程,都会对应一个父进程,而这个父进程可以复制多个子进程。例如www服务器。
3)每个进程都可能以两种方式存在的。前台与后台,所谓前台进程就是用户目前屏幕上可以进行操作的。后台进程则是实际在操作,但是由于屏幕无法看到的进程,通常用后台方式执行。
4)一般系统的服务都是以后台的进程方式存在,而且都会常驻在系统中,直到关机才结束。
# 显示系统执行的进程
# 说明
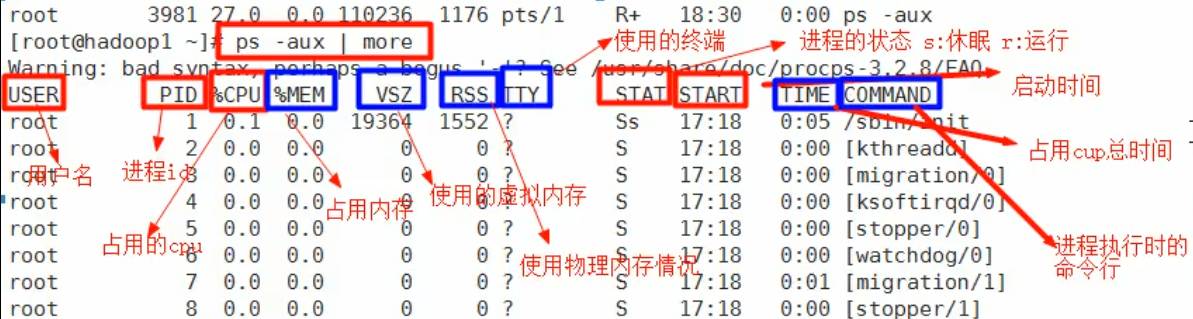
查看进程的指令是:ps,一般使用的参数是 ps -aux 。ps命令是用来查看目前系统中有哪些进程正在执行,以及他们执行的状况。可以不加任何参数。
ps显示的信息选项:
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PID | 进程识别号 |
| TTY | 终端机号 |
| TIME | 此进程所消CPU时间 |
| CMD | 正在执行的命令或进程名 |
ps -a:显示当前终端的所有进程信息ps -u:以用户的格式显示进程信息ps -x:显示后台进程运行的参数
# ps详解
1)指令:ps -aux | grep xxx ,比如有没有sshd服务:ps -aux | grep sshd
2)指令说明
- System V展示风格
- USER:用户名称
- PID:进程号
- %CPU:进程占用CPU的百分比
- %MEM:进程占用物理内存的百分比
- VSZ:进程占用虚拟内存的大小(单位:KB)
- RSS:进程占用物理内存的大小(单位KB)
- TTY:终端名称的缩写
- STAT:进程状态,其中S-睡眠,s-表示该进程是会话的先导进程,N表示进程拥有比普通优先级更低的优先级,R-正在运行,D-短期等待,Z-僵死进程,T-被跟踪或者被停止等。
- START:进程启动时间
- TIME:CPU时间,即进程使用cup的总时间
- COMMAND:启动进程所用的命令和参数,如果过长会被截
# 应用实例
以全格式显示当前所有的进程,查看进程的父进程。
ps -ef 是以全格式显示当前所有的进程
-e 显示所有的进程。-f全格式。
ps -ef | grep xxx 是BSD风格
- UID:用户ID
- PID:进程ID
- PPID:父进程ID
- C:CPU用于计算执行优先级的因子。数值越大,表明进程是CPU密集型运算,执行优先级会降低;数值越小,表明进程是I/O密集型运算,执行优先级会提高
- STIME:进程启动的时间
- TTY:完整的终端名称
- TIME:CPU时间
- CMD:启动进程所用的命令和参数
# 终止进程kill和killall
# 介绍
若是某个进程执行一半需要停止时,或是已消除了很大的系统资源时,此时可以考虑停止该进程。使用kill命令来完成此项任务。
# 基本语法
kill [选项] 进程号
功能描述:通过进程号杀死进程killall 进程名称
功能描述:通过进程名称杀死进程,也支持啊是通配符,这在系统因负载过大而变得很慢时很有用
2
3
# 常用选项
-9:表示强迫进程立即停止
# 最佳实践
案例1:踢掉某个非法登入用户
[root@hadoop01 ~]# ps -aux | grep sshdroot
1077 0.0 0.2 112900 4312 ? Ss 18:05 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -Droot
1331 0.0 0.2 158904 5608 ? Ss 18:05 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0root
1923 0.0 0.2 158904 5608 ? Ss 21:07 0:00 sshd: root@pts/1root
2044 1.7 0.2 158904 5544 ? Ss 22:18 0:00 sshd: jack [priv]jack
2048 0.0 0.1 158904 2316 ? S 22:18 0:00 sshd: jack@pts/2root
2071 0.0 0.0 112824 972 pts/1 S+ 22:18 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd
[root@hadoop01 ~]# kill 2048
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
案例2:终止远程登录服务sshd,在适当时候再次重启sshd服务
[root@hadoop01 ~]# ps -aux | grep sshdroot
1077 0.0 0.2 112900 4312 ? Ss 18:05 0:00 /usr/sbin/sshd -Droot
1331 0.0 0.2 158904 5608 ? Ss 18:05 0:00 sshd: root@pts/0root
1923 0.0 0.2 158904 5608 ? Ss 21:07 0:00 sshd: root@pts/1root
2044 1.7 0.2 158904 5544 ? Ss 22:18 0:00 sshd: jack [priv]jack
2048 0.0 0.1 158904 2316 ? S 22:18 0:00 sshd: jack@pts/2root
2071 0.0 0.0 112824 972 pts/1 S+ 22:18 0:00 grep --color=auto sshd
[root@hadoop01 ~]# kill 1077
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
案例3:终止多个gedit编辑器
[root@hadoop01 ~]# killall gedit
案例4:强制杀掉一个终端
[root@hadoop01 ~]# ps -aux | grep bashroot
1331 0.0 0.1 115540 2076 pts/0 Ss 22:26 0:00 -bashjack
1361 0.0 0.1 115664 2044 pts/1 Ss+ 22:27 0:00 -bashroot
1384 0.0 0.0 112824 976 pts/0 S+ 22:27 0:00 grep --color=auto bash
[root@hadoop01 ~]# kill -9 1331
2
3
4
5
# 查看进程树pstree
# 基本语法
pstree [选项] ,可以更加直观的来看进程信息
# 常用选项
-p:显示进程的PID-u:显示进程的所属用户
# 应用实例
案例1:以树状的形式显示进程的pid
pstree -p
案例2:以树状的形式显示进程的用户id
pstree -u
# 服务(service)管理
# 介绍
服务(service)本质就是进程,但是是运行在后台的,通常都会监听某个端口,等待其他程序的请求,比如(mysql,sshd防火墙等),因此我们又称为守护进程,是Linux非常重要的知识点。
service管理指令
service 服务名 [start|stop|resart|reload|status]
# centos7后
systemctl [start|stop|resart|reload|status] 服务名
2
3
特别说明:在centos7后,不再使用service管理服务,而是systemctl。
# 实用案例
查看当前防火墙的状况,关闭防火墙和重启防火墙。
点击查看代码
# centos6的用法service iptables status
#查看防火墙状态service iptables stop
#停止防火墙service iptables start
#启用防火墙# centos7以后的用法
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 二 2021-01-12 22:26:45 CST; 35min ago
Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 759 (firewalld)
CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
└─759 /usr/bin/python2 -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid1月 12 22:26:42 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...1月 12 22:26:45 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.1月 12 22:26:45 hadoop01 firewalld[759]: WARNING: AllowZoneDrifting is enabled. This is considere...now.Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
# 关闭
[root@hadoop01 ~]#
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since 二 2021-01-12 23:02:36 CST; 11s ago
Docs: man:firewalld(1) Process: 759 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid $FIREWALLD_ARGS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 759 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)1月 12 22:26:42 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...1月 12 22:26:45 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.1月 12 22:26:45 hadoop01 firewalld[759]: WARNING: AllowZoneDrifting is enabled. This is considere...now.1月 12 23:02:34 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Stopping firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...1月 12 23:02:36 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Stopped firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
# 重启
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl restart firewalld
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since 二 2021-01-12 23:03:37 CST; 9s ago
Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 1581 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service
└─1581 /usr/bin/python2 -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid1月 12 23:03:37 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...1月 12 23:03:37 hadoop01 systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.1月 12 23:03:37 hadoop01 firewalld[1581]: WARNING: AllowZoneDrifting is enabled. This is consider...now.Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# centos7以后防火墙相关命令
启动: systemctl start firewalld
重启: systemctl reload firewalld 或者 firewall-cmd --reload
关闭: systemctl stop firewalld
查看状态: systemctl status firewalld 或者 firewall-cmd --state
开机禁用: systemctl disable firewalld
开机启用: systemctl enable firewalld
打开端口: firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
其中permanent表示永久生效,public表示作用域,8080/tcp表示端口和类型
关闭端口: firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-port=8080/tcp
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
防火墙开放3306端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanentfirewall-cmd --reload
命令含义:
--zone #作用域
--add-port=3306/tcp #添加端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议
--permanent #永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效
firewall-cmd --reload #并不中断用户连接,即不丢失状态信息
2
3
4
5
6
防火墙关闭3306端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=3306/tcp --permanent
命令含义:
--zone #作用域
--remove-port=3306/tcp #移除端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议
--permanent #永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效
2
3
4
5
查看已开放端口:firewall-cmd --list-all
[root@hadoop01 ~]# firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: ens33
sources:
services: dhcpv6-client ssh
ports: 22/tcp
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 细节讨论
1)关闭或者启用防火墙后,立即生效。[telnet 测试某个端口即可]
telnet 192.168.211.100 22
2)这种方式是临时生效,当重启系统后,还是会回归当前对服务的设置
3)如果希望设置某个服务自启动或关闭永久生效,要使用chkconfig指令
# 查看服务名称
方式1:使用setup ->系统服务
方式2:/etc/init.d/服务名称
centos6: ls -l /etc/init.dcontos7: systemctl list-unit-files
# 服务的运行级别(runlevel)
查看或者修改默认级别:vi /etc/inittab
Linux系统有7中运行级别(runlevel):常用的是级别3和5
运行级别0:系统停机状态,系统默认运行级别不能设置为0,否则不能正常启动
运行级别1:单用户工作状态,root权限,用于系统维护,禁止远程登录
运行级别2:多用户状态(没有NFS),不支持网络
运行级别3:完全的多用户状态(有NFS),支持网络
运行级别4:系统未使用,保留
运行级别5:X11控制台,登录后进入图形GUI模式
运行级别6:系统正常关闭并重启,默认运行级别不能设置为6,否者不能正常启动
思考 如果不小心将默认的运行级别设置为0或者7,怎么处理? 进入单用户模式,修改成正常即可。
# 开机运行流程

# chkconfig指令
介绍
通过chkconfig/systemctl命令可以给每个服务的各个运行级别设置自启动/关闭
在 Centos7 中 systemctl 是设置系统服务(service)的命令,它融合之前service和chkconfig的功能于一体。
chkconfig 和 systemctl 区别对比
| 任务 | 旧指令 | 新指令 |
|---|---|---|
| 使某服务自动启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd on | systemctl enable httpd.service |
| 使某服务不自动启动 | chkconfig --level 3 httpd off | systemctl disable httpd.service |
| 检查服务状态 | service httpd status | systemctl status httpd.service(服务详细信息) / systemctl is-active httpd.service (仅显示是否 Active) |
| 加入自定义服务 | chkconfig --add test | systemctl load test.service |
| 删除服务 | chkconfig --del xxx | 停掉应用,删除相应的配置文件 |
| 显示所有已启动的服务 | chkconfig --list | systemctl list-units --type=service |
| 启动某服务 | service httpd start | systemctl start httpd.service |
| 停止某服务 | service httpd stop | systemctl stop httpd.service |
| 重启某服务 | service httpd restart | systemctl restart httpd.service |
基本语法
1)查看服务chkconfig --list | grep xxx
# centos6
[root@hadoop01 ~]# chkconfig --list | grep sshd
# contos7
[root@hadoop01 ~]# systemctl list-unit-files | grep sshdsshd-keygen.service
static sshd.service
enabled sshd@.service
static sshd.socket
disabled
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2)chkconfig 服务名 --list
# centos6
[root@hadoop01 ~]# chkconfig iptables --list
2
3)chkconfig --level 5 服务名 on/off
# centos6
chkconfig --level 5 sshd off
2
# 应用实例
案例1:显示当前系统所有服务的各个运行级别的运行状态
chkconfig --listsystemctl list-unit-files
案例2:查看sshd服务运行状态
service sshd statussystemctl status sshd
案例3:将sshd服务在运行级别5下设置为不自动启动
chkconfig --level 5 sshd off
案例4:在当运行级别为5时,关闭防火墙
chkconfig --level 5 iptables off
案例5:所有运行级别下,关闭防火墙
chkconfig iptable offsystemctl stop firewalld
案例6:在所有运行级别下,开启防火墙
chkconfig iptable onsystemctl start firewalld
# 使用细节
chkconfig重新设置服务后自启动或关闭,需要重启机器reboot才能生效。
# 动态监控进程
# 介绍
top与ps命令很相似。他们都是用来显示正在执行的进程。top与ps最大的不同之处,在于top在执行一段时间可以更新正在运行的进程。
# 基本语法
top [选项]
# 选项说明
| 选项 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -d 秒数 | 指定top命令每隔几秒更新,默认是3秒在top命令的交互模式当中可以执行的命令 |
| -i | 使top不显示任何闲置或者僵死的进程 |
| -p | 指定监控进程ID来仅仅监控某个进程的状态 |
# 交互操作说明
| 操作 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| P | 以CPU使用率排序,默认就是此项 |
| M | 以内存的使用率排序 |
| N | 以PID排序 |
| q | 退出top |
# 应用实例
案例1:监视特定用户
top:输入此命令,按回车键,查看执行的进程。
u:然后输入"u"回车,再输入用户名,即可。
2
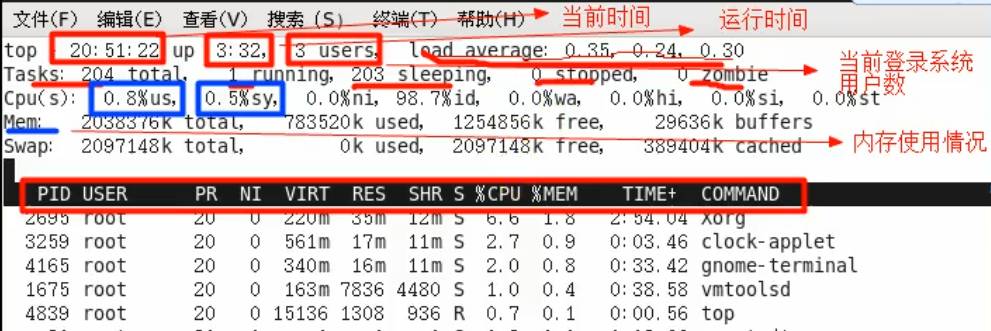
案例2:终止指定的进程。
top:输入此命令,按回车键,查看执行的进程。
k:然后输入"k"回车,再输入要结束的进程ID号。
2
案例3:指定系统状态更新的时间(每隔10秒自动更新,默认是3秒)
top -d 10
# 监控网络状态
# 查看系统网络情况netstat
基本语法
netstat [选项]netstat -anp
选项说明
-an:按一定顺序排列输出 -p:显示哪个进程在调用
应用案例
查看系统所有的网络服务
netstat -anp | more
查看服务名为sshd的服务的信息
netstat -anp | grep sshd
# 检测主机连接命令ping
是一种网络检测工具,它主要是用检测远程主机是否正常,或是两部主机间的介质是否为断、网线是否脱落或网卡故障。如:ping 对方ip 地址。
